Types of Material Handling Equipment
Material handling equipment is essential for moving, storing, controlling, and protecting goods throughout manufacturing, warehousing, and distribution processes.
In today’s material handling industry, the right machinery—from conveyors and cranes to automated systems—can transform operations by improving safety, reducing costs, and boosting productivity. This comprehensive guide explores the main types of material handling equipment, their functions, and best-use scenarios.
Transportation Equipment
Transportation devices move materials between locations or workstations. They form the backbone of any logistics layout, streamlining workflows and reducing manual labor.
Conveyors
Conveyors provide continuous movement of goods along a fixed path. Whether handling unit loads or bulk materials, they eliminate repetitive lifting and carrying:
-
Unit load conveyors transport pallets, cartons, or totes.
-
Bulk load conveyors handle loose materials like grains or pellets.
-
In-floor, on-floor, and overhead conveyors adapt to facility layouts, maximizing space and throughput.
Industrial Trucks
Industrial trucks—including pallet jacks, hand trucks, and forklifts—offer flexibility for variable routes and load sizes. These vehicles excel where conveyors cannot reach:
-
Pallet jacks are ideal for moving palletised goods over short distances.
-
Forklifts lift heavy loads onto racks and transport materials across the floor.
-
Order pickers and turret trucks enable workers to retrieve items from high shelves.
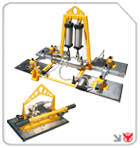
Overhead & Gantry Cranes
For lifting exceptionally heavy or oversized loads, cranes are indispensable. In particular, portable gantry cranes options allow you to move the crane structure to different work zones, combining capacity with flexibility. These systems excel in metal fabrication, automotive, and steel mill environments.
Jib Cranes
Mounted on columns or walls, jib cranes offer localized lifting with full rotation. Their compact footprint makes them ideal for small bays or work cells. Explore jib cranes wall-mounted solutions to add precise, 360° handling capability without major facility modifications.
Positioning Equipment
Positioning applications ensure materials are correctly placed for processing, assembly, or inspection—minimizing damage and enhancing quality control.
Hoists & Balancers
Hoists (manual, chain, or electric) lift loads vertically, while balancers maintain tension to hold items at a fixed height. These devices reduce worker fatigue and support fine adjustments during assembly tasks.
Manipulators & Industrial Robots
Advanced manipulators and industrial robots handle repetitive or hazardous tasks. From welding and palletizing to machine tending, these systems operate with precision and speed, freeing operators for higher-value work.
Ergonomic Lifting Tables
Height-adjustable lift tables and scissor lifts position heavy loads at optimal work heights. By eliminating bending and over-reaching, they reduce ergonomic risks and enhance throughput.
Unit Load Formation Equipment
Unit load devices consolidate products into single, manageable loads, simplifying transport and storage.
Pallets & Slip-Sheets
-
Pallets (wood, plastic, metal, or rubber) provide a stable base for stacking materials, compatible with forklifts and pallet jacks.
-
Slip-sheets are lightweight alternatives that reduce pallet costs and save space; they use tabs to secure bundles for handling.
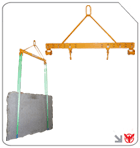
Lifting Clamps: Scissor & Slab Lifting Clamps
Lifting clamp attachments enable secure gripping of materials like steel beams, concrete slabs, and stone sheets. For example, scissor lifting clamps solutions and slab lifting clamps products from Aardwolf ensure stable, damage-free lifting. These clamps adjust to various thicknesses and automatically lock under load, making them indispensable lifting equipment in construction and fabrication.
Specialized Lifting Equipment
Specialized machines handle fragile, heavy, or awkward loads that standard conveyors and trucks cannot manage safely.
Vacuum Lifters
Vacuum lifters use suction cups to lift delicate materials—glass panels, stone slabs, and sheet metal—without clamps or slings. Their gentle yet firm grip minimizes surface damage. Explore the latest vacuum lifter technology for handling material that demands precision.
Scissor Lifters
Scissor lifters elevate loads vertically via a crisscross mechanism. They provide stable, adjustable height for transfer to and from conveyors, trucks, or worktables. Integrating scissor lifters into production lines maintains flow while protecting workers from manual lifting injuries.
Storage Equipment
Effective storage solutions organize inventory, optimize space, and streamline retrieval.
Racking Systems
-
Selective pallet racks for direct access to every pallet.
-
Double-deep and drive-in racks for higher density.
-
Cantilever racks for long or irregular loads.
Proper rack selection supports rapid picking and safe stacking.
Automated Storage & Retrieval Systems (ASRS)
ASRS combines vertical lift modules, mini-load cranes, and shuttle systems to store and retrieve goods with minimal aisle space. These material-handling systems increase storage density by up to 70% and reduce picking errors through precise automation.
Load Securing & Accessories
Securing loads is vital for safe transport, preventing shifting and damage.
Ratchet Tie-Down Straps
Ratchet tie down traps and heavy duty ratchet straps stabilize cargo on trucks, pallets, or racks. High-strength webbing and locking mechanisms ensure loads remain stationary under shock and vibration.
Dunnage & Protective Materials
Foam, edge protectors, and shrink wrap safeguard fragile items. Proper dunnage selection complements lifting clamps and vacuum lifters, delivering comprehensive protection.
Key Benefits Across the Material Handling Industry
Across every category, modern material handling equipment delivers measurable advantages:
-
Cost Savings: Automation reduces labor needs and damage-related losses.
-
Space Efficiency: Vertical stacking, ASRS, and overhead lifts maximize floor space.
-
Safety Improvements: Ergonomic devices and automated safeguards cut workplace injuries.
-
Productivity Gains: Continuous operation and precise placement accelerate workflows.
-
Scalability: Modular equipment adapts as volumes grow or processes change.
-
Competitive Edge: Leading material handling companies leverage cutting-edge solutions to outperform rivals.
Choosing the Right Material Handling Equipment
Selecting the optimal mix of machines requires a strategic approach:
-
Assess Material Types & Volumes
Identify weight, dimensions, fragility, and throughput requirements. -
Map Your Workflow
Optimize equipment placement to minimize travel distances and bottlenecks. -
Balance Cost & ROI
Calculate total cost of ownership, factoring in maintenance, energy, and productivity gains. -
Incorporate Automation
Leverage material-handling systems—conveyors, ASRS, AGVs—to reduce manual steps. -
Train & Maintain
Provide comprehensive operator training and preventive maintenance to maximize uptime.
Conclusion
From gantry crane material handling and conveyors to scissor lifters, vacuum lifters, and automated retrieval systems, the diversity of material handling equipment ensures that every facility can tailor solutions to its unique needs. By understanding the types, functions, and benefits of each category, businesses can enhance safety, reduce costs, and boost operational efficiency—driving sustainable growth in the fast-evolving landscape of material handling.












































Follow us on: