The Role of Material Handling Equipment
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, adopting lean manufacturing principles is essential for eliminating waste, optimizing workflows, and driving continuous improvement.
Introduction
Central to this approach is the strategic integration of material handling equipment throughout every stage of production. From basic lifting clamp mechanisms to sophisticated conveyor systems, the right infrastructure ensures components move seamlessly along the line, minimizing delays and maximizing throughput. As businesses across the material-handling industry vie to enhance productivity, investing in reliable material handling equipment solutions—from gantry cranes to vacuum lifter platforms —becomes a cornerstone of lean success. In this article, we explore how modern equipment designs drive efficiency, safety, and sustainability in lean environments.
Seamless Integration of Equipment and Processes
Achieving true lean manufacturing requires a unified system where processes and equipment function as one cohesive unit. By carefully mapping production workflows and material flows, manufacturers can select material handling equipment that aligns with takt times and takt flow principles.
Process Synchronization
Synchronizing equipment operations with production schedules reduces idle time and prevents bottlenecks. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs), conveyor modules, and overhead cranes can be orchestrated via Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) to ensure parts arrive exactly when needed, eliminating excess inventory and reducing work-in-process (WIP).
Equipment Compatibility
Integrating digital controls, IoT sensors, and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) with conveyors and lifting devices ensures real-time visibility into system performance. Moreover, optimizing gantry crane material handling configurations allows heavy or awkward loads to traverse work cells efficiently, minimizing manual interventions and line stoppages.
Scalable Layouts
Modular designs—such as portable gantry cranes and plug-and-play conveyor segments—facilitate quick reconfiguration of production lines. This scalability supports product mix changes without lengthy downtime, aligning closely with lean’s emphasis on flexibility and continuous improvement.
Enhancing Ergonomics and Safety
Ergonomics in lean manufacturing focuses on designing systems that amplify human capabilities while minimizing fatigue and injury risk. Well-designed material handling equipment plays a crucial role in achieving ergonomic excellence.
Reducing Manual Lifting
Heavy or repetitive lifting tasks are major sources of workplace injuries. Scissor lifting clamps devices and electric hoists reduce the need for manual exertion, lowering the incidence of musculoskeletal disorders and keeping operators focused on value-added activities.
Human–Machine Synergy
Controls and interfaces that are intuitive—such as ergonomically placed hand levers on slab lifting clamps—enhance precision and reduce cognitive load. By matching machine capabilities to human strengths, equipment designers help teams maintain high productivity without sacrificing safety.
Compliance and Standards
Premium material-handling equipment often exceeds regulatory requirements for load testing and guarding. Features such as emergency-stop circuits, load-holding valves, and safety interlocks ensure both compliance and peace of mind on the shop floor.
Driving Cost Efficiency in the Material-Handling Industry
Effective lean implementation isn’t just about speed—it’s about doing more with less. The right material handling equipment can substantially reduce both upfront and operating costs.
Lower Operating Expenses
Switching from fuel-powered to battery-operated forklifts and pallet jacks reduces energy costs and greenhouse gas emissions. Similarly, using automated systems cuts labor overhead and helps avoid expensive overtime.
Maintenance and Lifecycle Management
High-quality equipment from reputable material handling companies often comes with predictive-maintenance packages. Sensors monitor component wear and trigger service alarms before failures occur, minimizing unplanned downtime and expensive repairs.
Flexible Financing and ROI
Many suppliers offer leasing, rental, or pay-per-use models, enabling manufacturers to align capital expenditure with cash flow. When evaluated using total cost of ownership (TCO) analyses, investments in advanced material handling equipment often pay for themselves within months through efficiency gains and reduced scrap.
Minimizing Material Damage Through Advanced Handling Solutions
Damage to raw materials and finished goods during transport represents an irrecoverable cost. Specialized handling devices ensure that products arrive intact at each processing stage.
Vacuum and Slab Lifters
A dedicated vacuum lifter system enables non-porous sheet materials—such as glass, metal sheets, and stone—to be lifted without marks or scratches. When combined with slab lifting clamps, fragile items can be handled safely, reducing rework and waste.
Precision Clamping
Lifting clamp solutions, including scissor and beam-type clamps, apply controlled pressure to irregular or heavy loads. These devices stabilize cargo during transit and positioning, ensuring accurate placement on milling machines or assembly jigs.
Secure Transport
For over-the-road or inter-plant moves, heavy duty ratchet straps (often referred to as ratchet tie down traps) provide reliable load securing. Their high-tensile webbing and mechanical advantage eliminate cargo shift and protect both operators and products.
Promoting Environmental Sustainability
Lean manufacturing aligns closely with sustainability goals by reducing waste, energy consumption, and carbon footprints. Material handling equipment innovations contribute significantly to greener operations.
Energy-Efficient Drives
Variable-frequency drives (VFDs) on motors allow conveyors, cranes, and lifters to ramp smoothly, conserving energy during start-stop cycles. Coupled with regenerative braking in electric forklifts, facilities can capture and reuse power during deceleration phases.
Emission Reduction
Battery-powered and hydrogen-fuel-cell vehicles eliminate tailpipe emissions, helping manufacturers comply with stringent environmental standards such as those under the Paris Agreement. Deploying zero-emission equipment demonstrates corporate responsibility and can qualify operations for green incentives.
Waste Minimization
By preventing product damage and enabling precise material movement, advanced equipment reduces scrap rates. Fewer defects translate directly to less rework, lower material consumption, and a leaner environmental footprint.
Key Equipment for Lean Material Handling
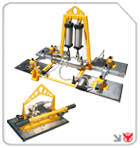
Gantry Cranes
Overhead gantry cranes systems offer excellent load capacities and span versatility, making them ideal for moving large assemblies across open bays. Their modular design supports customized heights and lengths tailored to specific work cells.
Jib Cranes
Compact jib cranes deliver localized lift-and-swing capability, perfect for repetitive tasks at machining stations or loading docks. Their wall- or column-mounted frames free up floor space and enable quick operator access.
Scissor Lifters
Scissor lifters and scissor lifting clamps devices provide vertical lift and tilt functions for pallets, molds, and skids. These units minimize bending and reaching, enhancing operator comfort and reducing cycle times.
Vacuum Lifters
A vacuum lifter uses suction cups and vacuum pumps to handle delicate or porous materials without mechanical grip points. Ideal for glass, stone, and sheet metal, these systems dramatically cut handling time and surface damage.
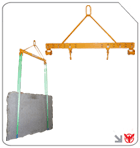
Slab Lifting Clamps
Heavy-duty slab lifting clamps secure stone, tile, and composite slabs for vertical or horizontal moves. Their jaw profiles adapt to varying thicknesses, ensuring safe transport and placement.
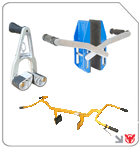
Lifting Clamps
Beam and universal lifting clamps provide robust gripping for steel plate, pipe bundles, and structural sections. Their simplicity and reliability make them indispensable in fabrication and warehousing environments.
Ratchet Tie-Down Straps
Also known as ratchet tie down traps, these heavy duty ratchet straps use high-strength webbing and mechanical advantage to secure loads during transit, preventing shifting and ensuring compliance with transport regulations.
Automated Guided Vehicles and Forklifts
Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and electric forklifts streamline repetitive material movements, reducing manual handling and supporting just-in-time (JIT) delivery. Their precise navigation and load-handling capabilities align perfectly with lean cell layouts.
H2: Partnering with Leading Material Handling Companies
Choosing the right supplier is as critical as selecting the equipment itself. Top material handling companies provide more than just hardware—they offer consultation, customization, and lifecycle support.
-
Consulting & Layout Design: Expert firms analyze facility layouts and material flows to recommend optimal equipment combinations.
-
Customization & Integration: Whether retrofitting an existing line or installing a greenfield site, reputable vendors tailor solutions that integrate with ERP and MES platforms.
-
Training & After-Sales Support: Comprehensive operator training, maintenance programs, and spare-parts logistics ensure continuous uptime and rapid response to issues.
-
Technology Roadmaps: Partners with strong R&D pipelines help future-proof installations by introducing IoT, predictive analytics, and automation upgrades over time.
Conclusion
Incorporating advanced material handling equipment is a fundamental driver of lean manufacturing success. By ensuring seamless integration, enhancing ergonomics, reducing costs, minimizing damage, and promoting sustainability, modern handling systems empower manufacturers to achieve higher efficiency and quality. From gantry cranes to jib cranes, scissor lifting clamps to vacuum lifters, each piece of equipment plays a strategic role in supporting lean goals. As you evaluate your material flows and production objectives, partnering with industry-leading equipment providers can unlock significant competitive advantages—transforming your facility into a model of lean excellence.












































Follow us on: