How to Master Material Handling in Supply Chain Efficiency
Material handling—the movement, storage, control and protection of materials and products throughout the supply chain—is the linchpin of operational excellence.
From raw materials entering a facility to finished goods leaving for distribution, every touch point influences lead times, costs and customer satisfaction. In today’s dynamic markets, material handling industry leaders and material handling companies must continuously refine processes, invest in the right lifting equipment and leverage automation to stay competitive.
Understanding Material Handling: The Backbone of Supply Chain Efficiency
What Is Material Handling?
Material handling encompasses the manual, semi-automatic and automatic activities required to move, store, protect and control goods from origin to consumption. It is the invisible thread that binds warehousing, distribution and production, ensuring products flow swiftly, safely and cost-effectively.
Why Material Handling Matters
Efficient material-handling equipment reduces waste, minimizes damage and speeds up throughput. When materials arrive at a dock, a robust system ensures they are quickly transferred, stored in optimal locations and retrieved for dispatch without delay. This efficiency translates into lower inventory levels, reduced labor costs and higher on-time delivery rates.
Types of Material Handling Systems
Manual Material Handling
In manual handling, workers use physical force to lift, carry or push loads. While still common, manual methods are prone to ergonomic injuries and bottlenecks when volumes surge.
Semi-Automatic Material Handling
Semi-automatic systems combine human oversight with machinery—like assisted conveyors that transport goods once placed on the belt. This hybrid approach balances flexibility with reduced physical strain.
Automatic Material Handling
Fully automated solutions—such as Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), robotic palletizers and intelligent conveyors—operate with minimal human intervention. These systems maximize throughput and accuracy, ideal for high-volume, repetitive tasks.
Essential Material Handling Equipment for Streamlined Operations
Forklifts, AGVs and Pallet Jacks
Traditional lift trucks and pallet jacks handle bulk movements, whereas AGVs navigate pre-defined paths to automate pallet transport, freeing personnel for value-added tasks.
Conveyors, Palletizers and Hoists
Conveyors move items along fixed routes; palletizers stack goods efficiently; hoists lift heavy assemblies. Integrating these devices creates continuous, high-speed workflows.
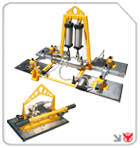
Crane Solutions: Gantry and Jib Cranes
For overhead loads, invest in overhead gantry cranes safety to combine mobility with load stability, or deploy wall-mounted jib cranes support when floor space is limited. Both solutions enhance gantry crane material handling capabilities and reduce manual lifting risks.
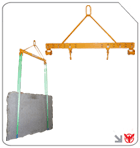
Specialized Lifting Equipment
-
Scissor Lifter & Slab Lifters: Secure and elevate stone, glass or sheet materials with the efficient Aardwolf scissor lifter or Aardwolf slab lifters, eliminating distortion and operator fatigue.
-
Vacuum Lifters: Use electric vacuum lifters for non-porous loads, ensuring damage-free handling.
-
Lifting Clamps: Attach to beams or rails to lift irregular items safely.
These specialized lifting equipment options bolster safety and precision for critical load profiles.
Best Practices for Mastering Material Handling
Ergonomic Lifting Techniques
Train staff to maintain a neutral spine, bend at hips and knees, and keep loads within the “power zone” (mid-thigh to mid-chest). This reduces back strain and injury risk when manually handling material.
Securing Loads with Tie-Downs
Prevent load shifts with robust solutions like the ratchet tie down straps. Proper anchoring safeguards both people and products during transport.
Planning Warehouse Layout
Design wide, unobstructed aisles for forklifts and AGVs. Zone storage areas by frequency of access and group similar items to streamline pick paths and reduce handling material touchpoints.
Implementing Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
Document workflows for every operation—receiving, storage, picking, packing and shipping. Consistent SOPs reinforce safe, efficient use of material-handling equipment and maintain regulatory compliance.
Integrating Advanced Technologies to Boost Efficiency
Automation and Robotics
Adopt robotics for palletizing, order picking and container unloading. Pair lift trucks with AMRs to automate horizontal transport, seamlessly blending human-driven and robotic operations.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Implement warehouse management systems (WMS) and IoT sensors to track load movements, monitor equipment performance and predict maintenance needs. Analytics reveal bottlenecks, enabling continuous improvement in handling material flows.
Future Trends in the Material Handling Industry
Emerging technologies—like AI-driven sortation, digital twins and autonomous cranes—promise further gains in accuracy, safety and flexibility. Material handling companies that pilot these innovations will shape the next era of supply chain efficiency.
By mastering the selection of the right material-handling equipment, adopting ergonomic and safety best practices, and integrating advanced automation, businesses can transform material handling from a cost center into a competitive advantage. Implement these strategies to optimize workflows, safeguard your workforce and achieve unparalleled supply chain efficiency.












































Follow us on: