5 Steps for Material Handling Safety at Your Warehouse
Material handling—the movement, storage, control and protection of materials throughout the supply chain—is the backbone of efficient warehouse operations.
In the material handling industry, incorrect practices can lead to costly injuries and product damage, disrupting workflows and eroding profit margins. From small material handling companies to large distribution centers, implementing safety protocols not only protects workers but also boosts productivity and ensures compliance with regulatory standards
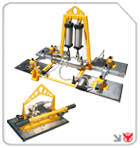
Across warehouses, a blend of manual labor and powered devices—ranging from forklifts and pallet jacks to vacuum lifter slab lifter units and gantry cranes—facilitates high throughput. Yet without rigorous controls, specialized lifting equipment such as a lifting clamp, scissor lifter, or complex gantry crane material handling systems can introduce risks like pinch points, dropped loads and ergonomic strain. The following five-step safety framework leverages best practices from industry leaders and regulatory bodies to help you safeguard personnel, streamline operations and maximize the ROI of your material-handling equipment.
Step 1: Assess Risks Before Material Handling
Conduct a Thorough Material Handling Risk Assessment
Before any manual or mechanical handling task, perform a comprehensive risk assessment. Identify the load characteristics—weight, size, shape—and determine if they exceed manual handling limits or require a powered aid. Assessing risks and planning your approach is the first and most critical principle of manual handling safety. Identify Equipment-Related Hazards
Evaluate hazards associated with each device in your workflow. For instance, a vacuum lifter slab lifter can minimize direct contact, but suction failure poses drop risks; lifting clamp attachments and scissor lifter mechanisms may introduce pinch-point hazards; gantry crane material handling systems require clear swing radii to prevent collisions. Document these hazards and establish controls—guards, emergency stops and exclusion zones—before operations begin.
Step 2: Master Proper Material Handling Techniques
Ergonomic Lifting Techniques for Handling Material
Whether stacking cartons or positioning pallets, workers must maintain a neutral spine, engage core muscles and lift with the legs. Keeping loads close to the body and avoiding twisting motions to reduce back strain—practices that can cut musculoskeletal injuries by up to 60%.
Adopt Manual Handling Principles
Incorporate the “five principles” of safe manual handling—Plan, Position, Pick, Proceed and Place—to create muscle-friendly workflows. Clearing pathways, stable footing and smooth, deliberate motions to protect both staff and inventory when shifting bulky or irregular loads.
Step 3: Utilize Material Handling Equipment Safely
Select and Operate Mechanical Aids
Powered equipment reduces manual strain and accelerates throughput. For moving heavy pallets, consider forklifts or pallet jacks. To lift and position overhead loads safely, deploy cranes: invest in portable gantry cranes enhance safety that offer flexibility and dependability, or mount jib cranes wall-mounted support if floor space is limited, Before operation, always inspect mechanical aids for wear, fluid leaks and functioning safety devices.
Integrate Specialized Lifting Equipment
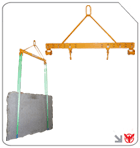
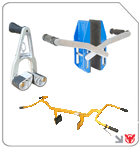
For delicate or awkward shapes, incorporate advanced tools: secure stone slabs with Aardwolf scissor lifting clamps equipments or Aardwolf slab lifters ASL-105 products, and handle non-porous surfaces using Electric vacuum lifter AVLP4 products. These lifting equipment solutions eliminate direct load contact, reducing fatigue and damage risk
Step 4: Secure Loads with Effective Material Handling Tools
Use Ratchet Straps and Tie-Downs
Proper load securing prevents shifting during transport. Equip pallets and flatbeds with heavy-duty straps—ratchet tie down traps—and follow proven methods to protect both freight and bystanders. Learn how right heavy duty ratchet straps improve load stability and reduce slippage incidents
Employ Proper Clamping Devices
When lifting irregular or sheet-like loads, clamp attachments are indispensable. A well-adjusted lifting clamp can secure a load without over-compression, while a scissor lifter ensures vertical alignment. Regularly inspect jaws, pads and locking mechanisms to prevent accidental release
Step 5: Optimize Warehouse Layout for Material Handling
Design Safe Material Flow Paths
Efficient warehouse layouts minimize unnecessary movements and reduce congestion. Plan aisles wide enough for powered vehicles, designate clear staging areas for in-process loads, and integrate logical zones for handling material to follow a smooth path from receiving to dispatch. Strategic placement of cranes or conveyors can enhance both safety and throughput
Schedule Regular Equipment Inspection and Maintenance
Preventive maintenance preserves the integrity of both manual and powered handling systems. Establish inspection intervals for cranes, hoists, clamps and tie-down devices, and document findings to comply with requirements and internal quality standards
By systematically assessing risks, training teams, leveraging the right material-handling , securing loads correctly and optimizing your warehouse layout, you create a resilient safety culture. These five steps help material handling companies reduce injury rates, safeguard valuable cargo and drive operational excellence in the material handling industry.












































Follow us on: